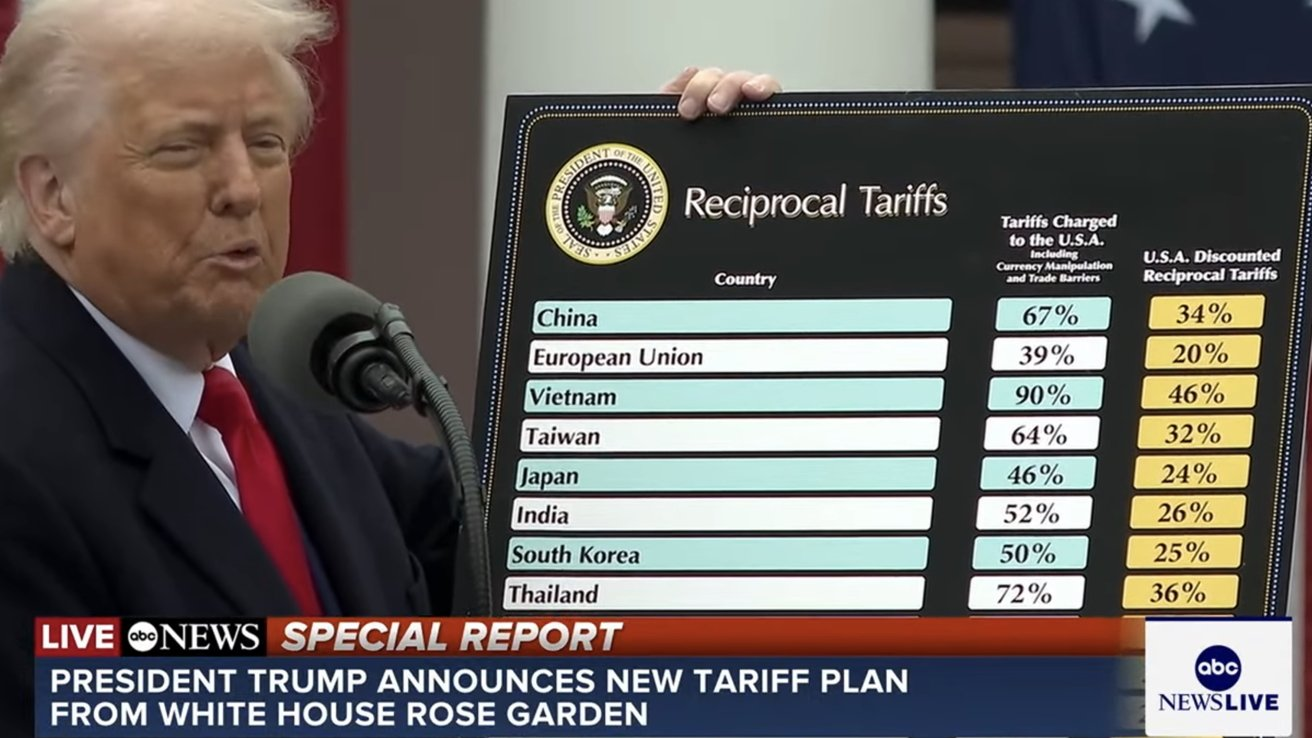
In 2024, the Trump administration announced “strategic-level tariffs” on Chinese imports, with electronic consumer goods facing duties as high as 46%. By early April 2025, these tariffs had escalated to 54%, triggering seismic shifts in the global supply chain. As the world’s largest manufacturing hub for phone accessories—accounting for 75% of global phone case production—China’s dominance is now at a critical inflection point, with ripple effects reshaping the industry landscape.
Cost Restructuring: The Dissolution of the “China Price” Advantage
- Financial records from a mid-sized phone case factory in Shenzhen Longgang District reveal stark changes: the FOB price for U.S.-bound 0.35mm ultra-thin polycarbonate (PC) phone cases surged from $1.8 to $2.6 per unit. This seemingly modest $0.8 increase erodes 12% of net profit margins on orders of tens of millions of units. Compounding the pressure, U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) has intensified inspections, raising X-ray screening rates from 3.7% in 2020 to 19.2% in Q1 2024, extending average customs clearance times to 37 days—a 2.8x increase from pre-tariff levels.
- This dual squeeze has accelerated “geographical arbitrage” in manufacturing. Taiwan-owned Catcher Technology, based in Dongguan, relocated 35% of its CNC precision engraving capacity to Vietnam’s Bac Giang Province, leveraging Vietnam’s 6.8% average tariff rate for U.S. exports. However, relocation costs remain steep: Vietnamese factory workers achieve only an 82% welding pass rate, far below China’s 97% benchmark (IDC 2024 Supply Chain Report). By April 2025, Vietnam’s cost advantage evaporated as the U.S. imposed 46% tariffs on Vietnamese imports.
Brands’ Strategic Dilemma: The Boundary Effects of Cost Shifting
- Consumer market repercussions are already visible: After Anker raised prices for its bestselling shockproof phone case on Amazon from $14.99 to $18.99, sales plummeted by 23% (Jungle Scout data). Price elasticity varies sharply across segments: premium brands like Mous Limited maintained a 6% price increase for carbon fiber series due to lower price sensitivity among high-end consumers, while generic $5-range products suffered 17% market share losses.
- This pressure is forcing supply chain innovation. Apple’s “tariff-immune” production model, piloted at Foxconn’s Zhengzhou facility, ships semi-finished phone cases to Ciudad Juárez, Mexico, for final assembly. By leveraging the USMCA agreement, Apple achieves tariff-free U.S. access despite a $0.4 per-unit logistics cost increase—still favorable compared to 46% tariffs (Bloomberg Supply Chain Analysis).
The Butterfly Effect of Industrial Migration: Technology Spillover and New Cluster Emergence
- China’s manufacturing exodus is creating opportunities for technology diffusion. Tata Group’s smart factory in Haryana, India, integrated Huawei’s 5G+ Industrial Internet solutions to slash mold development cycles from 45 days to 22 days. This technological leap drove India’s phone case exports to surge by 184% year-on-year in the first half of 2024 (India Electronics Association).
- Deeper transformations are occurring in materials science: Tesla’s 4680 battery tabless design has been adapted to phone case mold engineering, boosting injection molding yields to 99.3%. Dongguan ABON’s liquid silicone rubber (LSR) integrated molding process reduced energy consumption by 37% while cutting production cycles to 8 seconds per unit.
The Equation for Building a Resilient Supply Chain
Current industrial transformation reveals three key trends:
- Distributed Manufacturing: Shein’s “small-order, fast-response” model is expanding into hardware. Shenzhen-based AliExpress sellers now achieve 72-hour customized delivery via 3D-printing micro-factories.
- Tariff Arbitrage Networks: The emerging Penang-Monterrey “Dual Springboard” logistics corridor (Malaysia to Mexico) cuts total costs by 19% compared to direct China-U.S. shipping.
- Intelligent Compliance Systems: Alibaba.comAI Tariff Engine calculates optimal customs solutions across 3,000+ product variants in real time.
Survival Rules for the New Industrial Cycle
Future industry leaders will share three traits:
- – “Manufacturing Chameleons”: Mastery of multi-regional production agility.
- – “R&D Adaptogens”: Strategic reserves of material substitution technologies.
- – “Data Navigators”: Advanced digital compliance architectures.
As Boston Consulting Group (BCG) noted in 2024 Global Supply Chain Reset: “Tomorrow’s winners won’t be the lowest-cost producers, but those with the highest elasticity coefficients.”
The upheaval in the phone case industry epitomizes the digital transformation of global manufacturing. Tariff policies are not merely disrupting cost structures but dismantling the foundational logic of traditional global division of labor. Enterprises that plant seeds of innovation in the fissures of tariff barriers will ultimately thrive in the reborn industrial ecosystem.